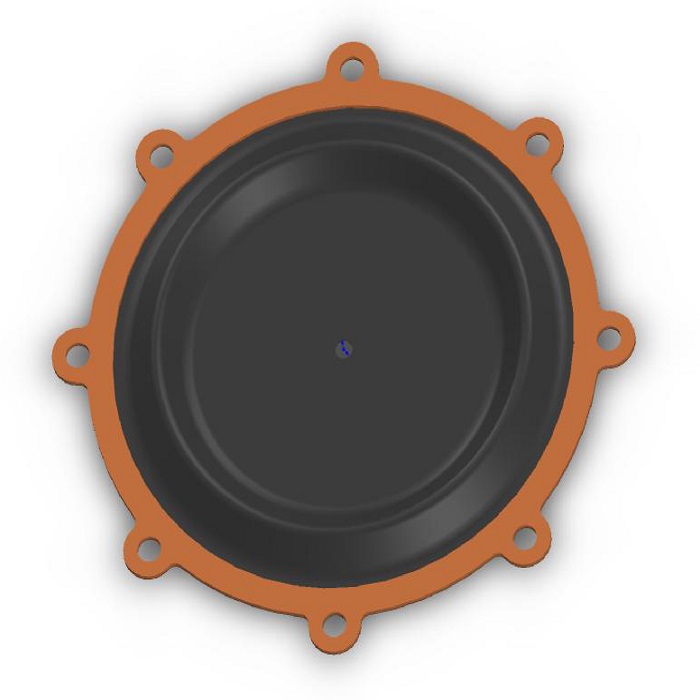
Rubber Diaphragm

Rubber diaphragm for Pneumatic Regulator Actuator
A rubber diaphragm is a sealant that acts as a movable diaphragm to prevent leakage and friction between two or more parts. They come in a variety of sizes, sizes and shapes.
Rubber diaphragms are used in various fields such as pharmaceuticals, gas regulation, energy processing, automotive food and beverage manufacturing. Also, these diaphragms are available in different polymer lifetimes Viton, Silicone, EPDM, Neoprene, etc.
We started producing rubber diaphragms in 1990 and entered the international market in 2007. We have been working on diaphragm technology, overcoming some difficult products, and providing customers with world-class rubber diaphragms.With decades of expertise, our engineers work with customers to design and manufacture rubber diaphragms using the latest tools and techniques.
Customers’ drawings or samples are always welcome for quote and manufacture.
Categories:Diaphragm Products Tags: Rubber Diaphragm Seals
| Diaphragm | ||
| Function | Seal for Automotive, Machine, Valve, Electrical Appliances, etc. | |
| Material | NR, NBR, HNBR, EPDM, Silicone, ACM, AEM, FKM, FVMQ, etc. diaphragm for regulator | |
| Color | Black (recommended), but other color available | |
| Hardness | 20~90 Shore A diaphragm for regulator | |
| Certificates | RoHS, PAHS, REACH, FDA, KTW, NSF, WRAS, CCS, EN681-1, National Sanitary Certificate | |
| Size | DN max = 2000mm, all other smaller sizes will per customer demands diaphragm for regulator | |
| Properties (Optional and Multiple) |
Oil Resistance, Chemical Resistance, Steam Resistance, Aging Resistance, Heat Resistance, Cold Resistance, Fire Resistance, Environment Protective, Strong Resilience, Abrasion Resistance, etc. | |
Rubber Diaphragm size list
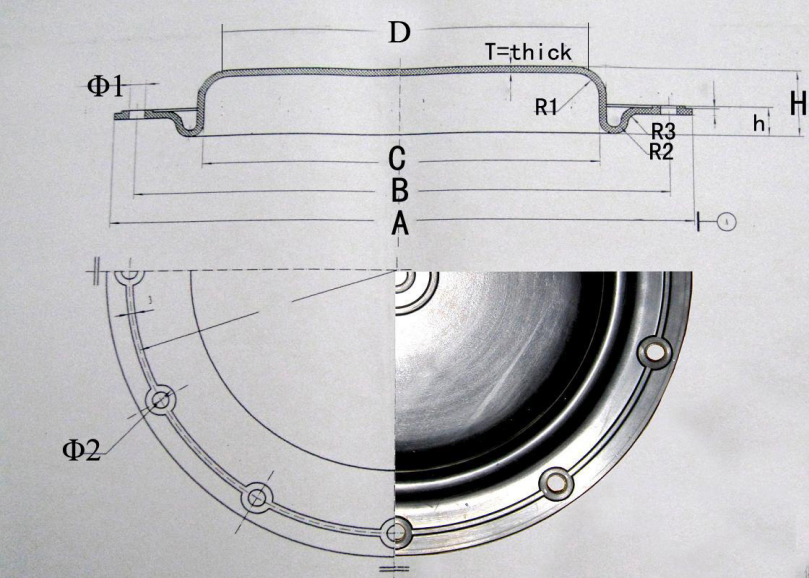
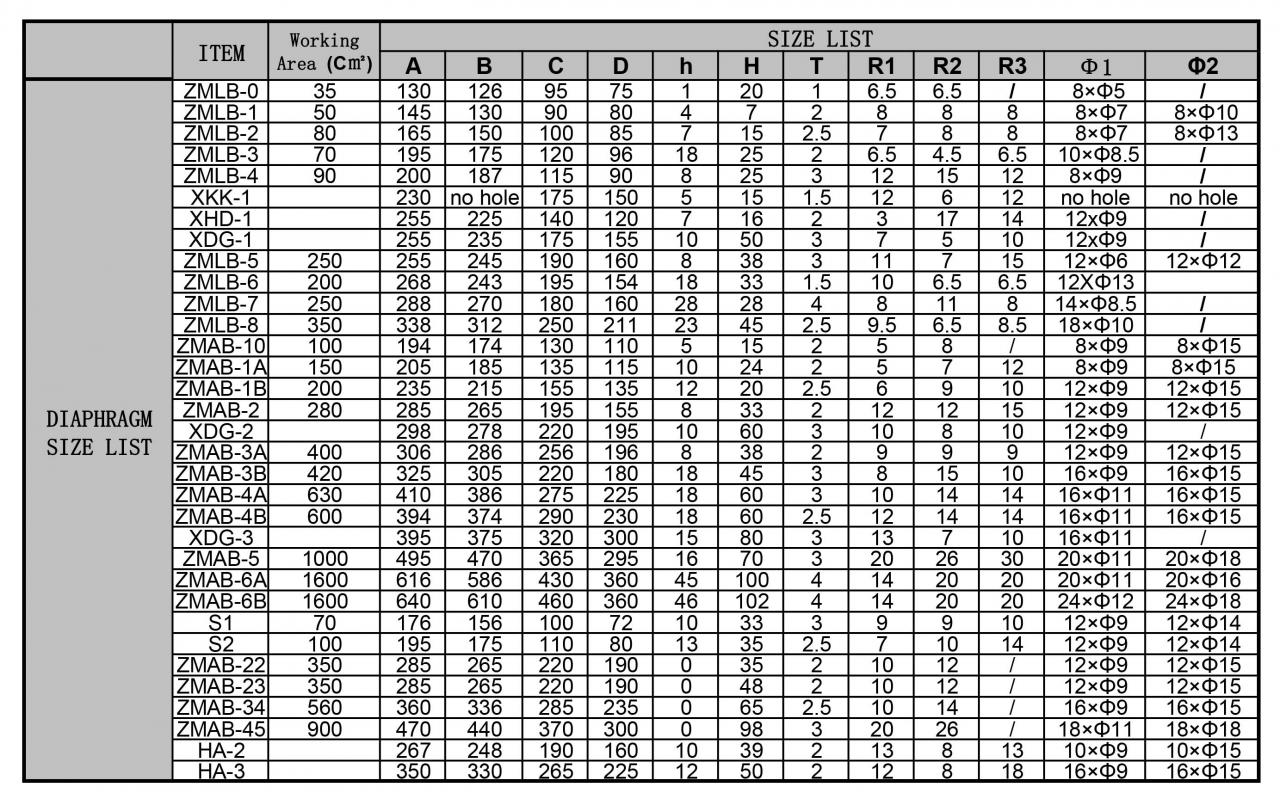
Rubber diaphragms are versatile and flexible sealing components that provide variable sealing in flow control type applications. When pressure is applied from the outside, the rubber compresses to form a seal, controlling flow or pressure. Rubber diaphragms allow for easy and accurate control of air, water and other fluids as well as dust and other gases.
We are one of the leading rubber diaphragm manufacturers in China, producing various single and composite elastomers of rubber diaphragms that can be adapted to many industry applications.
What are the main uses and application areas of rubber diaphragm?
Pressure regulation and control: Usually used for pressure regulators and control systems.
Pump and valve: Rubber diaphragm is an integral part of diaphragm pump and valve. They form seals and provide the necessary flexibility to control fluid flow, making them ideal applications in the chemical, pharmaceutical, and food industries.
Automotive industry: In automobiles, used for systems such as brake boosters and fuel pumps.
Hydraulic and pneumatic systems: Rubber diaphragms are used for hydraulic and pneumatic actuators, which are crucial in heavy machinery, construction equipment, and industrial automation.
Medical devices: They exist in medical devices such as sphygmomanometers, ventilators, and infusion pumps, playing a crucial role in controlling and regulating fluid flow.
Water treatment: Water treatment plants use diaphragm valves to control the flow and distribution of water and chemicals.
Chemical processing: Suitable for processing various chemicals and corrosive substances, making them valuable in chemical processing equipment.
The oil and gas industry: They are used for control systems, managing oil and natural gas flows, ensuring safety and reliability.
Instruments and measurements: Use rubber diaphragms in pressure sensors and transducers to accurately measure pressure.
Environmental engineering: It can be used in wastewater treatment systems, air pollution control equipment, and equipment in seawater desalination plants.
Food and Beverage Industry: Diaphragm pumps use food grade rubber diaphragms for safe and hygienic transportation and processing of food and beverages.
What are the key characteristics of rubber diaphragm in engineering and industry that make them so important in different applications?
Rubber diaphragms are important in various applications due to these key characteristics:
1. Rubber diaphragms have high flexibility and elasticity, allowing them to deform and bend under changes in pressure or fluid flow. This characteristic enables them to effectively regulate and control the flow of gases or liquids.
2. Rubber diaphragms are renowned for their excellent sealing performance. They can form a reliable seal between two components to prevent leakage and ensure the containment of fluids, gases, or other substances.
3.Many rubber materials used in the diaphragm have chemical resistance and are suitable for handling various chemicals, including corrosive and abrasive substances.
4. Durable and able to withstand stress from repeated bending, pressure difference, and mechanical wear.
5. Depending on the specific rubber material, the diaphragm can provide good resistance to extreme temperatures.
6.In industries such as food and pharmaceuticals, food grade rubber diaphragms can be used. Their design complies with strict hygiene standards, making them safe to use in sensitive applications.
7. It has strong corrosion resistance and usually uses rubber diaphragms instead of metal diaphragms.
8. It has low friction characteristics and is suitable for applications that require minimal resistance and wear, such as pumps and valves.
9.The damping characteristics of rubber enable it to effectively reduce noise and vibration in the system, improve the overall efficiency and comfort of industrial equipment.
10.Rubber is usually non-conductive, which is valuable in electrical applications that require insulation.
How does the selection of diaphragm materials affect the performance and durability of rubber diaphragm? What are the common diaphragm material options?
The selection of diaphragm materials significantly affects the performance and durability of rubber diaphragms, as different materials offer varying properties suited to specific applications.
Common diaphragm material options and their impact on performance include:
Natural Rubber (NR): Natural rubber diaphragms are known for their high flexibility and elasticity. They provide good tear resistance and are suitable for applications that require low pressure, such as in pneumatic systems. However, they may not be as resistant to chemicals and environmental factors as synthetic rubbers.
Neoprene (CR): Neoprene diaphragms are valued for their excellent resistance to oils, greases, and moderate chemicals. They offer good weather and ozone resistance, making them suitable for outdoor applications. Neoprene has good mechanical strength and durability.
Nitrile (NBR): Nitrile rubber diaphragms are highly resistant to oil, fuel, and other hydrocarbon-based fluids. They are commonly used in hydraulic and pneumatic systems, as well as in the automotive industry. NBR diaphragms have good tensile strength and wear resistance.
EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer): EPDM diaphragms are known for their exceptional resistance to weathering, ozone, and UV exposure. They are suitable for outdoor and environmental sealing applications. EPDM offers good electrical insulating properties.
Viton (FKM): Viton diaphragms have excellent resistance to a wide range of chemicals, including aggressive acids and solvents. They are often used in demanding chemical processing and industrial applications. Viton offers high-temperature resistance.
Silicone (VMQ): Silicone rubber diaphragms are known for their high-temperature resistance, making them suitable for high-heat applications. They also exhibit excellent flexibility and resistance to UV and ozone. However, they may not be as chemically resistant as other materials.
Hypalon (CSM): Hypalon diaphragms are valued for their resistance to chemicals, including acids, bases, and oxidizing agents. They are used in applications requiring durability and chemical resistance.
Butyl (IIR): Butyl rubber diaphragms have excellent resistance to gases and moisture, making them suitable for applications requiring air or gas containment, such as in pneumatic systems and pharmaceuticals.
Polyurethane (PU): Polyurethane diaphragms are known for their high wear resistance and durability. They are used in applications involving abrasive materials and where long diaphragm life is essential.
How resistant is the rubber diaphragm to temperature and chemical exposure?
The resistance of a rubber diaphragm to temperature and chemical exposure depends on the specific type of rubber material used in its construction. Different rubber materials have varying degrees of resistance to temperature and chemicals.
Temperature Resistance:
Natural Rubber (NR): Limited temperature resistance; typically not suitable for high-temperature applications.
Neoprene (CR): Good resistance to moderate temperatures, typically up to 250°F (121°C).
Nitrile (NBR): Good resistance to moderate temperatures, typically up to 250°F (121°C).
EPDM: Excellent resistance to high and low temperatures, typically from -40°F (-40°C) to 300°F (150°C).
Viton (FKM): Exceptional high-temperature resistance, often exceeding 400°F (204°C).
Silicone (VMQ): Excellent high-temperature resistance, typically from -70°F (-57°C) to 450°F (232°C).
Hypalon (CSM): Good temperature resistance, typically up to 250°F (121°C).
Butyl (IIR): Good resistance to low and moderate temperatures, typically from -40°F (-40°C) to 250°F (121°C).
Polyurethane (PU): Good resistance to temperature, but performance can vary depending on the specific formulation.
Chemical Resistance:
Natural Rubber (NR): Limited chemical resistance; not suitable for many chemicals.
Neoprene (CR): Good resistance to oils and moderate chemicals.
Nitrile (NBR): Good resistance to oils and hydrocarbon-based fluids.
EPDM: Limited resistance to hydrocarbon-based fluids but good resistance to ozone and weathering.
Viton (FKM): Excellent chemical resistance to a wide range of aggressive chemicals.
Silicone (VMQ): Limited chemical resistance, sensitive to certain solvents and chemicals.
Hypalon (CSM): Excellent resistance to acids, bases, and oxidizing agents.
Butyl (IIR): Good resistance to gases and moisture, limited resistance to oils and solvents.
Polyurethane (PU): Chemical resistance can vary based on the specific polyurethane formulation.
Custom Engineered Diaphragms for Industrial Needs
General Sealtech designs and produces diaphragm components for applications such as fuel systems, pumps, actuators, valves, regulators, and precision meters. Whether you’re seeking a replacement or developing a new device, we can work from your drawing, sample, or functional description to create custom solutions.
We specialize in many kinds of elastomer materials including NBR, EPDM, silicone, PTFE, FKM, HNBR, and other varieties. Reinforcements of polyester, nylon, cotton, and Nomex fabrics are added for improved strength and performance whenever necessary. Our team assists in material selection according to the operating condition—temperature, pressure, media to which it is exposed, and environmental exposure. Each of our orders is finished with mixing, molding, and quality control which guarantees variation uniformity, consistency, and contamination free results.





